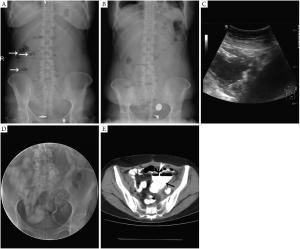
Demonstration of a sigmoid colon fistula using CT with gastrografin enema
Abstract
Intestinal fistula is one of the serious complications after surgery. The strategies of treatment are different according to the location, size, and number of intestinal fistula. We present a case of sigmoid colon fistula which occurred after surgery and chemotherapy for ovarian cancer. In this case, CT with gastrografin enema showed the exact location of the fistula.
Keywords
Intestinal fistula; computer tomography; enema
A 53-year-old woman was diagnosed with ovarian cancer, then underwent the hysterectomy plus lateral adnexectomy and received postoperative chemotherapy. One month later, the patient experienced abdominal pain and low fever. At the local clinics, the patient was diagnosed with intestinal obstruction based on abdominal X-ray, and was prescribed immediately for fast and gastrointestinal decompression. One day later, with an abdominal X-ray re-examination, the feature of intestinal obstruction disappeared. However, the patient’s abdominal pain aggravated, and body temperature was 39 °C. Localized tenderness and rebound tenderness on left lower abdomen were noted during physical examination. Plain CT showed the encapsulated effusion in left pelvic cavity. Patient was transferred to one tertiary hospital and underwent punctured drainage of encapsulated effusion under ultrasound guidance. According to the medical history, symptoms and medical examinations, the patient was diagnosed with intestinal fistula. Gastrointestinal series didn’t show small intestinal fistula. Plain CT with gastrografin enema showed that fistula was located in the back wall of sigmoid colon, which was confirmed by surgery. The patient had partialcolectomy for treatment.